Guardrails Configuration#
This section describes how to configure guardrails in the config.yml file to control LLM behavior.
The rails Key#
The rails key defines which guardrails are active and their configuration options.
Rails are organized into five categories based on when they trigger during the guardrails process.
Rail Categories#
The following table summarizes the different rail categories and their trigger points.
Category |
Trigger Point |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Input rails |
When user input is received |
Validate, filter, or modify user input |
Retrieval rails |
After RAG retrieval completes |
Process retrieved chunks |
Dialog rails |
After canonical form is computed |
Control conversation flow |
Execution rails |
Before/after action execution |
Control tool and action calls |
Output rails |
When LLM generates output |
Validate, filter, or modify bot responses |
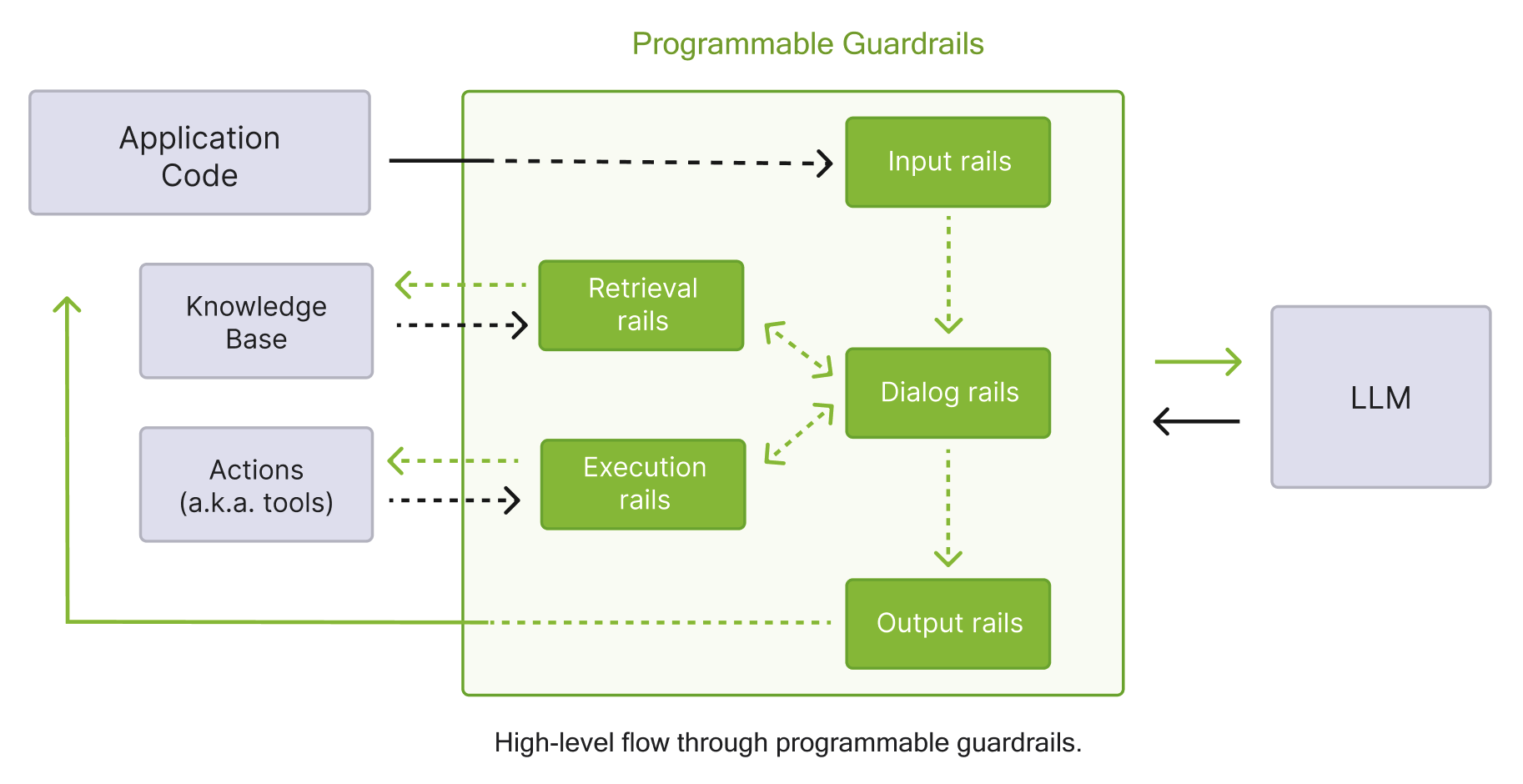
The following diagram shows the guardrails process described in the table above in detail.
Basic Configuration#
rails:
input:
flows:
- self check input
- check jailbreak
- mask sensitive data on input
output:
flows:
- self check output
- self check facts
- check output sensitive data
retrieval:
flows:
- check retrieval sensitive data
Input Rails#
Input rails process user messages before they reach the LLM:
rails:
input:
flows:
- self check input # LLM-based input validation
- check jailbreak # Jailbreak detection
- mask sensitive data on input # PII masking
For a complete list of available input flows, refer to the ../configuration-reference.md#input-rails.
Output Rails#
Output rails process LLM responses before returning to users:
rails:
output:
flows:
- self check output # LLM-based output validation
- self check facts # Fact verification
- self check hallucination # Hallucination detection
- mask sensitive data on output # PII masking
For a complete list of available output flows, refer to the ../configuration-reference.md#output-rails.
Retrieval Rails#
Retrieval rails process chunks retrieved from the knowledge base:
rails:
retrieval:
flows:
- check retrieval sensitive data
For a complete list of available retrieval flows, refer to the ../configuration-reference.md#retrieval-rails.
Dialog Rails#
Dialog rails control conversation flow after user intent is determined:
rails:
dialog:
single_call:
enabled: false
fallback_to_multiple_calls: true
user_messages:
embeddings_only: false
For a complete list of available dialog flows, refer to the ../configuration-reference.md#dialog-rails.
Execution Rails#
Execution rails control custom action and tool invocations:
rails:
execution:
flows:
- check tool input
- check tool output
Rail-Specific Configuration#
Configure options for specific rails using the config key:
rails:
config:
# Sensitive data detection settings
sensitive_data_detection:
input:
entities:
- PERSON
- EMAIL_ADDRESS
- PHONE_NUMBER
output:
entities:
- PERSON
- EMAIL_ADDRESS
# Jailbreak detection settings
jailbreak_detection:
length_per_perplexity_threshold: 89.79
prefix_suffix_perplexity_threshold: 1845.65
# Fact-checking settings
fact_checking:
parameters:
endpoint: "http://localhost:5000"
YAML Schema#
Complete guardrails configuration example:
rails:
# Input validation
input:
flows:
- self check input
- check jailbreak
- mask sensitive data on input
# Output validation
output:
flows:
- self check output
- self check facts
# Retrieval processing
retrieval:
flows:
- check retrieval sensitive data
# Dialog behavior
dialog:
single_call:
enabled: false
# Rail-specific settings
config:
sensitive_data_detection:
input:
entities:
- PERSON
- EMAIL_ADDRESS
- CREDIT_CARD
output:
entities:
- PERSON
- EMAIL_ADDRESS
Parallel Execution of Input and Output Rails#
You can configure input and output rails to run in parallel. This can improve latency and throughput.
When to Use Parallel Rails Execution#
Use parallel execution:
For I/O-bound rails such as external API calls to LLMs or third-party integrations.
If you have two or more independent input or output rails without shared state dependencies.
In production environments where response latency affects user experience and business metrics.
When Not to Use Parallel Rails Execution#
Avoid parallel execution:
For CPU-bound rails; it might not improve performance and can introduce overhead.
During development and testing for debugging and simpler workflows.
Configuration Example#
To enable parallel execution, set parallel: True in the rails.input and rails.output sections in the config.yml file. The following configuration example is tested by NVIDIA and shows how to enable parallel execution for input and output rails.
Note
Input rail mutations can lead to erroneous results during parallel execution because of race conditions arising from the execution order and timing of parallel operations. This can result in output divergence compared to sequential execution. For such cases, use sequential mode.
The following is an example configuration for parallel rails using models from NVIDIA Cloud Functions (NVCF). When you use NVCF models, make sure that you export NVIDIA_API_KEY to access those models.
models:
- type: main
engine: nim
model: meta/llama-3.1-70b-instruct
- type: content_safety
engine: nim
model: nvidia/llama-3.1-nemoguard-8b-content-safety
- type: topic_control
engine: nim
model: nvidia/llama-3.1-nemoguard-8b-topic-control
rails:
input:
parallel: True
flows:
- content safety check input $model=content_safety
- topic safety check input $model=topic_control
output:
parallel: True
flows:
- content safety check output $model=content_safety
- self check output
streaming:
enabled: True
chunk_size: 200
context_size: 50
stream_first: True
streaming: True