Guardrail Types#
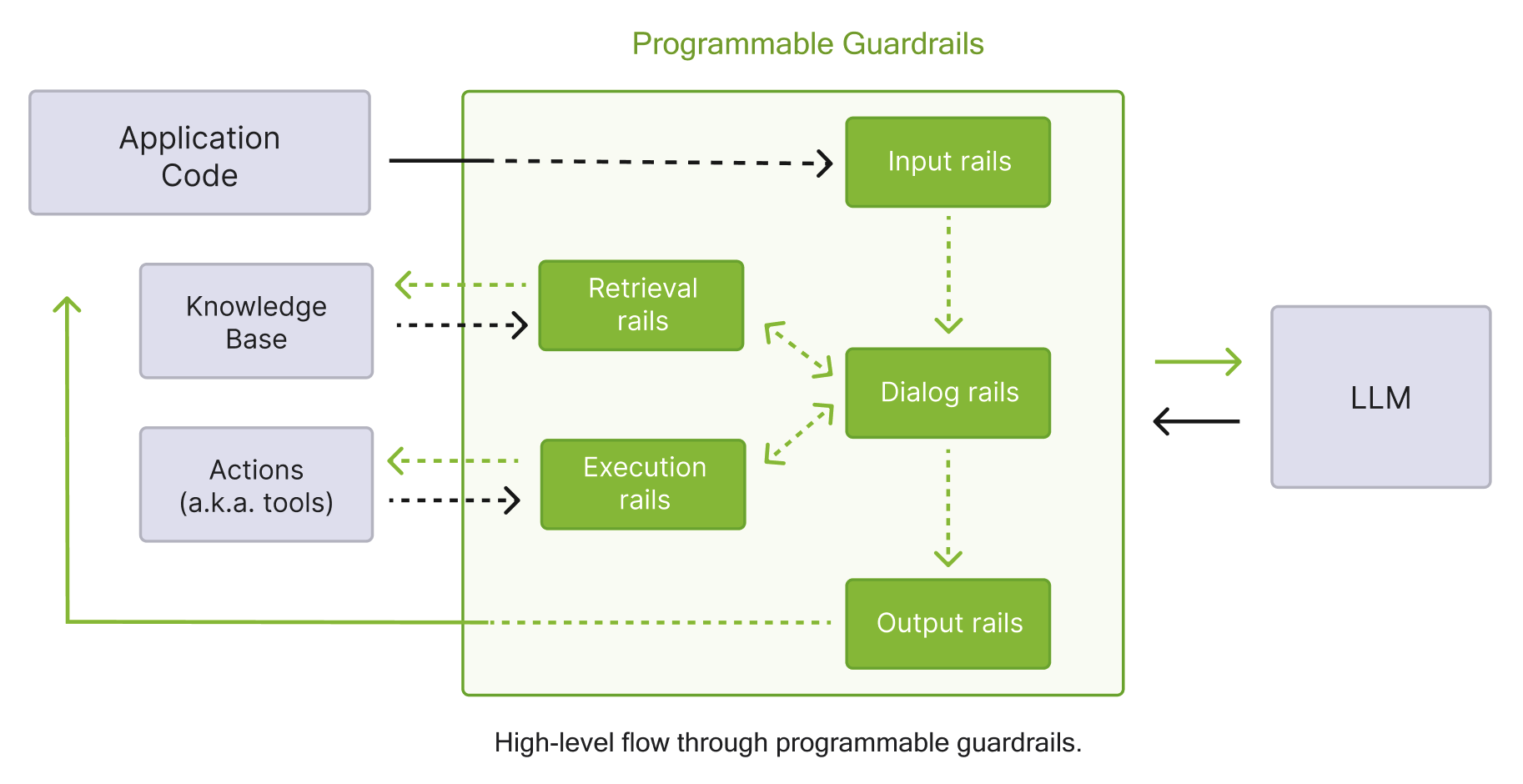
The NeMo Guardrails library applies guardrails (also called rails) at multiple stages of the LLM interaction. Input rails apply guardrails before the LLM is called by validating and sanitizing user inputs. Retrieval rails filter and validate retrieved knowledge (documents and chunks) to ensure only trusted context is provided to the LLM. Dialog rails steer and constrain the multi‑turn conversation, enforcing flow logic and policies across turns. Execution rails control and validate tool/function calls, their arguments, and results to safely interact with external systems. Output rails evaluate and post‑process model responses, filtering, editing, or blocking unsafe or off‑policy content before it reaches users.
Input and Output rails are the most common.
Stage |
Rail Type |
Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
Before LLM |
Input rails |
Content safety, jailbreak detection, topic control, PII masking |
RAG pipeline |
Retrieval rails |
Document filtering, chunk validation |
Conversation |
Dialog rails |
Flow control, guided conversations |
Tool calls |
Execution rails |
Action input/output validation |
After LLM |
Output rails |
Response filtering, fact checking, sensitive data removal |
Use Cases and Applicable Rails#
The following table summarizes which rail types apply to each use case.
Use Case |
Input |
Retrieval |
Dialog |
Execution |
Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Content Safety |
✅ |
✅ |
|||
Jailbreak Protection |
✅ |
||||
Topic Control |
✅ |
✅ |
|||
PII Detection |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
||
Knowledge Base / RAG |
✅ |
✅ |
|||
Agentic Security |
✅ |
||||
Custom Rails |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |